YOU ARE HERE Home > Blogs > Work Flow of E Invoice
Work Flow of E Invoice
GST DOST's BLOG

| Resource | E-invoicing |
The flow of the e-invoice generation, its registration and receipt of confirmation can be logically divided into two major parts:
a) The first part being the interaction between the business (supplier in case of invoice) and the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
b) The second part is the interaction between the IRP and the GST/E-Way Bill Systems and the Buyer.
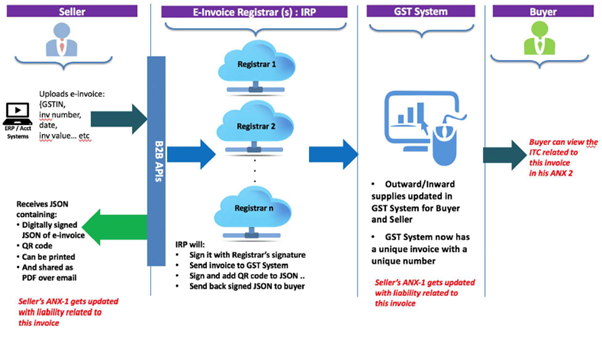
The two parts of the workflow are depicted diagrammatically below and followed up with an explanation of the steps involved. As the process evolves and system matures the same would be intercommunicated between buyer’s software and seller’s software, banking systems etc.
Part A: Flow from Supplier (commonly known as seller) to IRP.
Step 1
is the generation of the invoice by the seller in his own accounting or billing system (it can be any software utility that generates invoice including those using excel or GSTN’s provided Offline Utility). The invoice must conform to the e-invoice schema (standards) that is published and have the mandatory parameters. The optional parameters can be according to the business need of the supplier. The supplier’s (seller’s) software should be capable to generate a JSON of the final invoice that is ready to be uploaded to the IRP. The IRP will only take JSON of the e-invoice.
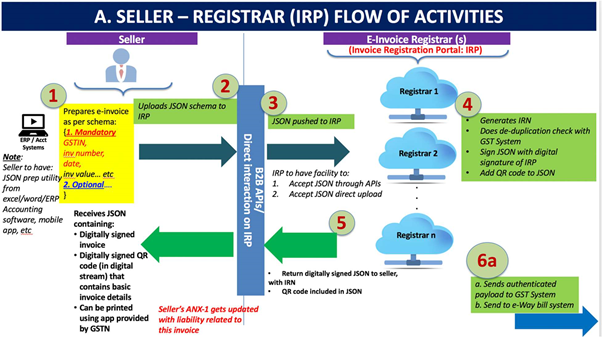
Note:
1. The seller should have a utility that will output invoice data in JSON format, either from his accounting or billing software or his ERP or excel/word document or even a mobile app. Those who do not use any accounting software or IT tool to generate the invoice, will be provided with an offline tool to key-in data of invoice and then submit the same.
2. The small and medium-size taxpayers (having annual turnover below Rs 1.5 Crores) can avail accounting and billing system being offered by GSTN free of cost.
Step 2 and 3:
is to upload and push the JSON of the e-invoice to the IRP by the seller. The JSON may be uploaded directly on the IRP or also through GSPs or through third party provided apps.
Step-4:
The IRP will generate the hash (IRN) based on seller’s GSTIN, Document Type, Document Number and Financial Year and check the hash from the Central Registry of GST System to ensure that the same document (invoice etc.) from the same supplier pertaining to same Fin Year is not being uploaded again. On receipt of confirmation from Central Registry, IRP will add its signature on the Invoice Data as well as a QR code to the JSON. The QR code will contain GSTIN of seller and buyer, Invoice number, invoice date, number of line items, HSN of the major commodity contained in the invoice as per value, hash etc (pl refer section on details of QR code below). The hash computed by IRP will become the IRN (Invoice Reference Number) of the e- invoice. This shall be unique to each invoice and hence be the unique identity for each invoice for the entire financial year in the entire GST System for a taxpayer. [GST Systems will create a central registry where hash sent by all IRPs will be kept to ensure uniqueness of the same].
In case the same document has been uploaded earlier, the IRP will send an error code back to the seller, when he tries to upload a duplicate e-invoice.
Step 5
will involve returning the digitally signed JSON with IRN back to the seller along with a QR code.
Step 6
will involve sharing the uploaded data of accepted document (invoice etc.) with GST and e-way bill system. More details are given in Part-B below.
Part B: Flow from IRP to GST System/E-Way Bill System & Buyer
The following diagram shows how e-Invoice data would be consumed by GST System for generation of e-way bill or populating relevant parts GST Returns, stated in Step-6 above.
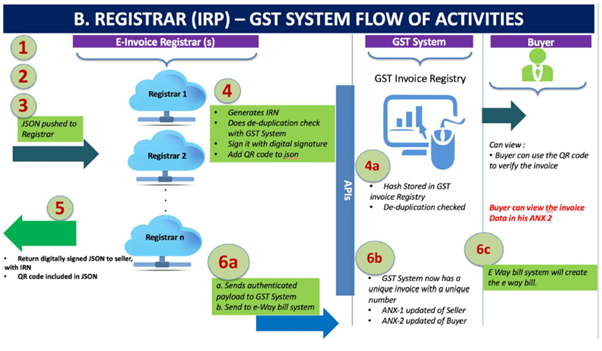
Step 6 (a)
will be to send the signed and authenticated e-invoice data along with IRN (same as that has been returned by the IRP to the seller) to the GST System as well as to E-Way Bill System.
Step 6 (b)
The GST System will update the ANX-1 of the seller and ANX-2 of the buyer, which in turn will determine liability and ITC.
Step 6 (c)
The e-invoice schema includes parameters e.g. ‘Transporter Id’ and ‘Vehicle Number’, etc. that are required for creating and generating e-way bills. Provision has also been made to enter transporter code and vehicle number, if available with the seller at the time of generation of e-invoice. In that case, the e-way bill can be prepared fully. The E-Way bill system will accordingly create e-way bill using this data.
Note 1:
The e-invoice standardized schema has mandatory and optional items. The e-invoice shall not be accepted in the GST System unless all the mandatory items are present. The optional items are to be used by the seller and buyer as per their business need to enforce their business obligations or relationships.
Note 2:
Seller may send his e-invoice for registration to more than one registrar. But the GST system and IRP will perform a de-duplication check with central registry to ensure that the IRN that is generated is unique for each invoice. Therefore, the IRP shall return ONLY ONE registered IRN for each invoice to the seller. In case of multiple registrars (more than one IRPs) only one IRP will return a valid IRN to the seller. Except one, all other IRPs will reject the request of registration.
Note 3:
The QR code will enable quick view, validation and access of the invoices from the GST system from hand held devices.
Small taxpayers, whenever so mandated, can use one of the eight free accounting/billing software currently listed by GSTN. Also, GSTN will provide Offline Tools where data of an invoice, generated on paper can be entered which in turn will create JSON file for uploading on the IRP. This upload to the IRP will also happen through APIs. Taxpayers may also use one of the many commercially available accounting / billing software for this purpose. All accounting and billing software companies are being separately asked to adopt the e-invoice standard so that their users can generate the JSON from the software and upload the same on the IRP.

Allahabad High Court Provides Relief to Businesses in Landmark GST e-Way Bill Ruling. [News]
GST Amnesty Scheme: A Golden Opportunity, But Heed the Advisory - Tax Samachar [News]
Madras High Court Quashes ITC Claim Rejection Based Solely on GSTR-3B and Directs Authorities to Consider Other Returns like GSTR 2A and GSTR 9. [Blog]
Supreme Court Upholds Statutory Immunity for Officers Under GST Act: A Closer Look at the Landmark Decision [Blog]
Consultant के Foreign Client पर GST का Impact [Video]
Goods Transport Agency और Multimodel Transporter अलग अलग है [Video]


